Public Health in India
Public Health is the science of improving and protecting the health of people and their communities where they work, live, learn and play. The public health professionals perform three core functions namely- the assessment, policy development, and assurance of the health of the whole population. The primary aim of these professionals is to reduce human suffering and to prevent people from getting injured or sick in contrast with doctors and nurses who treat people after they become sick. Public health workers conduct educational programs, research, encourage healthy behaviors and recommend policies to improve quality of life and promote healthcare accessibility and equity.
India Public Health Standards
In 2005, the National Rural Health Mission (NHM) came into power with the aim to strengthen the public health system in rural areas. The primary focus of the mission is to provide good quality health care to the rural population across the country with special emphasis on the states or union territories with weak healthcare infrastructure and public health indicators. The Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) guidelines drive the continuous improvement of quality and act as the benchmark for the assessment of the functional status of health facilities. Some of the general principles of IPHS are:
- The health needs of the entire district should be considered while designing the primary and secondary health care services at public facilities.
- The district hospital should be adequately equipped and staffed to meet the large portion of secondary healthcare needs the district’s population such that only a small proportion would require a referral to high-level tertiary care centers.
- For each district the total number of healthcare facilities will be dependent on its total population, geographical need, local epidemiology, time to care, and community requirements.
- There should be a District Health Action Plan (DHAP) in every district, in which health facilities are identified and mapped listing the level and type of services they provide.
- Implementation of all national programs at each facility centre should be in alignment with the latest Government of India/state guidelines developed for that program.
NGO's working in Public Health in India
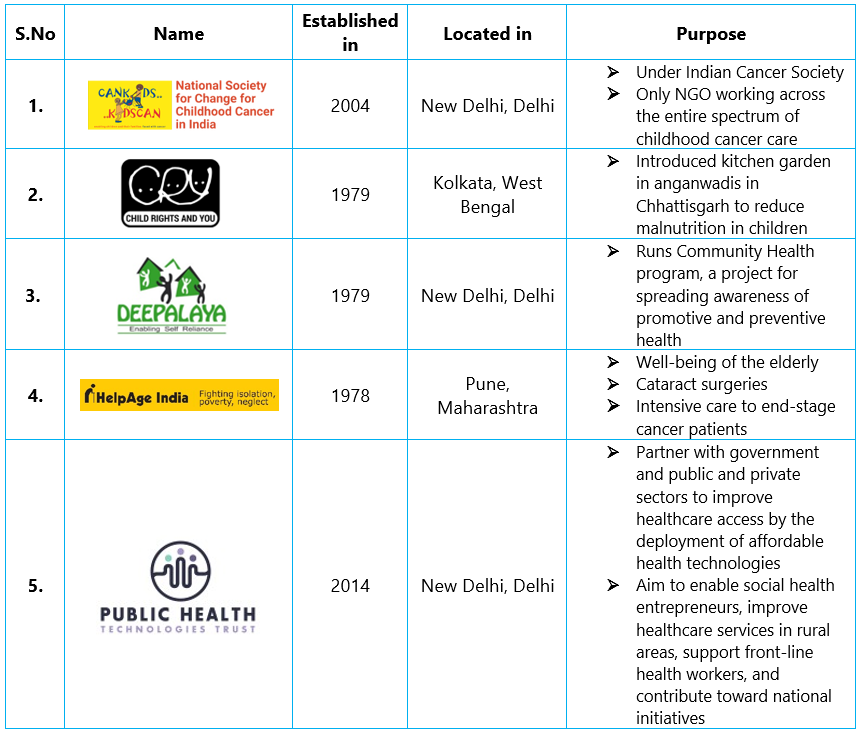
According to a paper published in 2016, 60% of the Non-Government Organizations (NGO’s) function primarily in the health sector. Several NGOs are working in different healthcare sectors like nutrition, child and reproductive health, treatment of communicable diseases and early identification of diseases. The following is the list of NGOs In India who are working in Public Health:

Conclusion
In recent years, India has seen a change in perspective related to public health. People have started demanding better public health services and trust has been built that health services would improve in the coming years. The link between the private healthcare centers, the health insurance, and the public, needs to be strengthened to improve the healthcare sector in cities as well as those living far beyond. As the public health services will come more into force with more people trusting the public health system, the real progress would be seen in India’s health. The main aim of public health systems is to create a happier, healthier world where every individual can live up to their full potential.
Related Post: Neurological Clinical Trial Trends Under Pandemic and Changing Geopolitics
Tags

Saurabh is a Senior Content Writer at PharmaShots. He is a voracious reader and follows the recent trends and innovations of life science companies diligently. His work at PharmaShots involves writing articles, editing content, and proofreading drafts. He has a knack for writing content that covers the Biotech, MedTech, Pharmaceutical, and Healthcare sectors.